Server on Android using Linux Deploy
A friend asked me how difficult it would be to run a python program 24/7 in his own network. I said easy, just use a Raspi. He answered: "I got an old phone with a broken touchscreen".
I've played around with Linux Deploy in the past, so I already knew it is possible to install Linux on an Android phone. I wasn't sure if python would run, but I was confident it's gonna work so I tried.
1. Setup
First thing: You need to have a rooted device.
I've used a Sony Z3 Compact.
The touch screen doesn't work anymore, but TWRP was already installed.
Luckily, because this was the only way to grant me ADB access by copying my key to /data/misc/adb/adb_keys.
I've used an USB-OTG cable to connect a mouse and control the pointer.
The following commands are all for Arch Linux, so if you decide to use another distro you need to adjust them.
So go ahead and install Linux Deploy on your rooted device.
On the configuration screen, I've made the following adjustments:
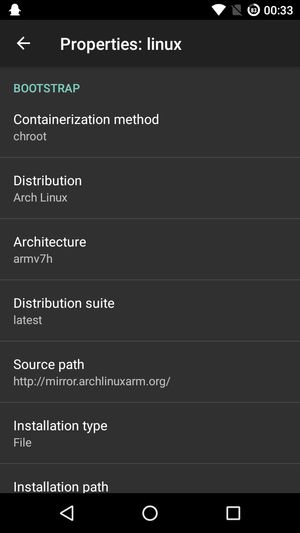
- Distribution: Arch Linux
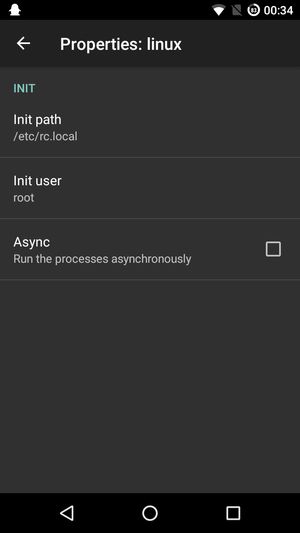
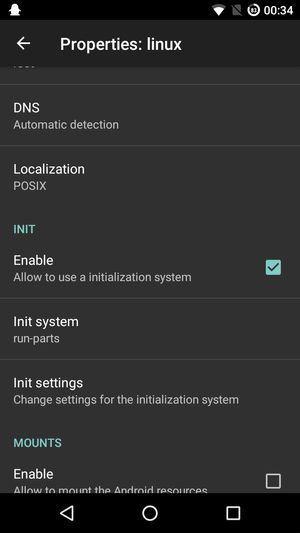
- Init: Enable, choose run-parts
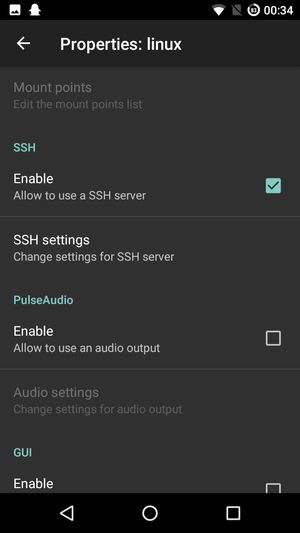
- SSH: Enable
Write the username and password down.
Create a new image with these settings and run it.
Next, try to establish a SSH connection ssh android@192.168.178.32.
If it works: Nice, you are now connected to an Arch Linux running on your phone.
The next steps for me was to install all dependencies for the software:
sudo pacman -S python2 python2-pip python2-requests procps
sudo pip2 install fake-useragentI've copied the software to the device (scp -r), and ran it by calling python2 myapp.py. Voilá.
2. Autostart
Now I also wanted the server to be started automatically when I power the phone on. This means two things: the linux container needs to be started, and also the software within it.
With run-parts, the /etc/rc.local is executed on container boot, as root. Mine now looks like this:
#!/bin/sh -e
su android -c '/home/android/run.sh'
exit 0So all I do is run another script in the home directory of the user.
#!/bin/sh -e
cd /home/android/
mkdir -p ./logs
python2 -u ./myapp.py > ./logs/myapp.log 2>&1 &This now leads to the start of myapp every time the container is started.
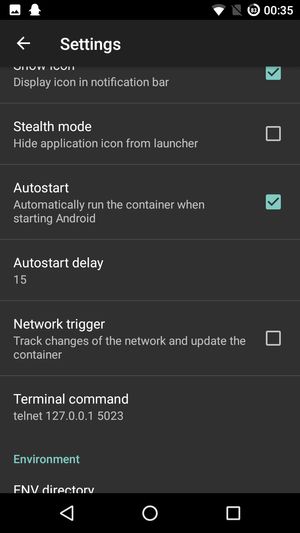
Last thing, to autostart the container on android boot, go to the Linux Deploy settings and enable Autostart. See screenshot below.
3. Limitations
You are limited in hardware access, because you are only within a chroot environment and Android controls the hardware.
However, for a simple use-case like a Flask application this should work fine.
4. Configuration
I've used version 2.1.0.