WiFi monitor mode
With monitor mode enabled, you can receive all packages on wireless networks around, without being connected to any. It is useful for debugging and security analysis.
I am very forgetful so I will just write down how to enable monitor mode for the devices I own.
1. Intel Dual Band Wireless-AC 8265 (iwlwifi)
Detailed explaination: sanilands.info/sgordon
iw dev
iw phy phy0 info # should show all information about the device, including the "monitor" capability
sudo iw phy phy0 interface add mon0 type monitor
ip link
sudo iw dev wlan0 del # (I had to replace wlan0 by wlp2s0)
sudo ip link set mon0 up
iw dev mon0 info
sudo iw dev mon0 set freq 2437 # set it to the right channelDetails
$ ls -lh /lib/firmware/iwlwifi-*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2,3M 8. Apr 17:31 iwlwifi-8265-21.ucode
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1,8M 8. Apr 17:31 iwlwifi-8265-22.ucode
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2,2M 8. Apr 17:31 iwlwifi-8265-27.ucode
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2,3M 8. Apr 17:31 iwlwifi-8265-31.ucode
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2,4M 8. Apr 17:31 iwlwifi-8265-34.ucode$ dmesg
[ 1.885451] Intel(R) Wireless WiFi driver for Linux
[ 1.885452] Copyright(c) 2003- 2015 Intel Corporation
[ 1.885536] iwlwifi 0000:02:00.0: enabling device (0000 -> 0002)
[ 1.886425] iwlwifi 0000:02:00.0: Direct firmware load for iwlwifi-8265-36.ucode failed with error -2
[ 1.886433] iwlwifi 0000:02:00.0: Direct firmware load for iwlwifi-8265-35.ucode failed with error -2
[ 1.889093] iwlwifi 0000:02:00.0: loaded firmware version 34.0.1 op_mode iwlmvm2. Samsung Galaxy S4 & Raspberry Pi 3
- Nexmon
- Native monitor mode in BCMDHD patch
- Nexmon for Raspberry Pi 3
- Ready-to-use image for Raspberry Pi 3
3. Macbook Air 2013 (Broadcom wl)
If you are on the wl driver, this is really simple. Just execute:
echo 1 | sudo tee /proc/brcm_monitor0And you should find another device prism0 next to your usual wlan0.
Use prism0 with Wireshark, Aircrack-ng or your favorite analysis tool.
4. Useful commands
4.1. Find network device
sudo lshw -C networkExample output
``` $ sudo lshw -C network *-network Beschreibung: Kabellose Verbindung Produkt: BCM4360 802.11ac Wireless Network Adapter Hersteller: Broadcom Corporation Physische ID: 0 Bus-Informationen: pci@0000:03:00.0 Logischer Name: wlan0 Version: 03 Seriennummer: 84:11:22:33:44:ff Breite: 64 bits Takt: 33MHz Fähigkeiten: pm msi pciexpress bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless Konfiguration: broadcast=yes driver=wl0 driverversion=6.30.223.271 (r587334) ip=192.168.178.38 latency=0 multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11 Ressourcen: irq:18 memory:b0600000-b0607fff memory:b0400000-b05fffff ```4.2. Find driver
lspci | grep -i wireless
lspci -vv -s 03:00.0 # replace with the numbers the previous command returnedExample output
```shell-session $ lspci -vv -s 03:00.0 03:00.0 Network controller: Broadcom Corporation BCM4360 802.11ac Wireless Network Adapter (rev 03) Subsystem: Apple Inc. BCM4360 802.11ac Wireless Network Adapter Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx- Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort-5. Frequency table
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_WLAN_channels
To show the current frequency used by your WiFi adapter, use either iwlist wlan0 channel or just plain iwconfig.
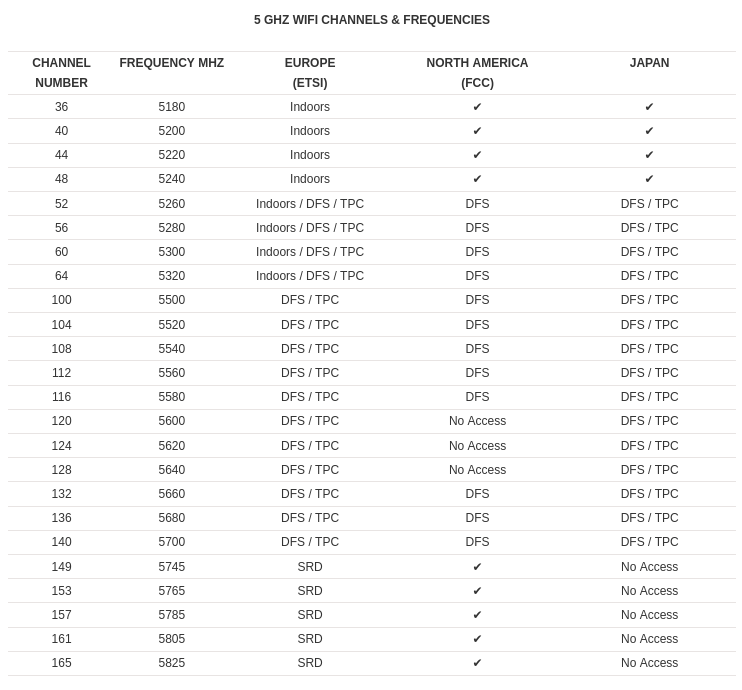
5.1. 2.4 GHz
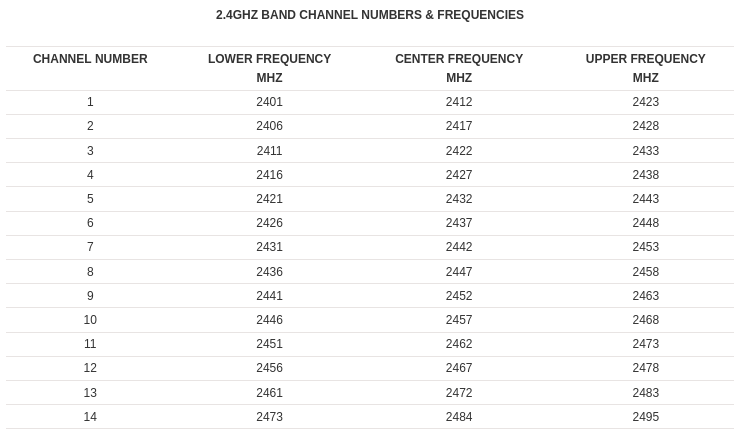
5.2. 5 GHz